The CLAIR Model: A Synthesized Conceptual Framework for Mapping Critical Infrastructure Interdependencies [Guest Diary]
[This is a guest diary contributed by Claire Perry (LinkedIn)]
The structural integrity of modern society is predicated upon a dense and often opaque network of interconnected systems. For decades, the modeling of these systems remained siloed within specific domains: industrial processes were governed by the hierarchical constraints of the Purdue Model, while corporate and data-centric ecosystems were organized using various Enterprise Architecture (EA) frameworks (Fortinet, n.d.; The Open Group, n.d.). However, the accelerating convergence of Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT) has exposed a critical analytical gap. Disruptions in the external utility grid, once considered an unlikely factor, now propagate through the physical and logical layers of the enterprise with devastating speed, as evidenced by recent power-related disconnections of large-scale data center operations (Mural et al., 2026; Islam et al., 2023).
To bridge this gap, this report introduces the Comprehensive Linkage and Architectural Infrastructure Resiliency (CLAIR) Model. The CLAIR Model is a new conceptual framework that synthesizes the vertical depth of the Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture (PERA) with the multi-dimensional, interrogative breadth of the Zachman Framework for Enterprise Architecture (Fortinet, n.d.; The Open Group, n.d.). By establishing a unified taxonomy that accounts for everything from the sub-physical utility grid to the hyper-distributed cloud, the CLAIR Model provides a structured scope for identifying and visualizing critical infrastructure interdependencies. This framework prioritizes the identification of these linkages over specific mitigations, offering a diagnostic tool for understanding how failures in one sector, such as the power grid, generate cascading effects across the data center and manufacturing landscapes (Fortinet, n.d.; Islam et al., 2023; Virginia Department of Emergency Management, n.d.).
Historical Context and the Necessity of Synthesis
The conceptual origin of industrial modeling lies in the 1990s at Purdue University, where researchers developed the Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture (PERA) to standardize computer-integrated manufacturing (Fortinet, n.d.). The Purdue Model established a functional hierarchy ranging from Level 0 (physical processes) to Level 4 (business logistics), effectively creating an "automation pyramid." Isolation of sensitive controllers from internet-facing business networks is typically achieved via a "demilitarized zone" (DMZ) at Level 3.5 (Fortinet, n.d.).
While the Purdue Model excels at describing the internal dependencies of a single plant, it is inherently insular. It treats the external world as a series of inputs (Level 0) or external services (Level 5) without mapping the complex, bidirectional relationships between the plant and the broader infrastructure (Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, 2025a; Williams, 1994). In parallel, Enterprise Architecture (EA) frameworks like Zachman were developed to organize the design artifacts of complex organizations from multiple stakeholder perspectives (The Open Group, n.d.). The CLAIR Model recognizes that neither framework, in isolation, can characterize the risks of a "system-of-systems" environment (Department of Defense, 2008). In modern critical infrastructure, a data center is not merely a facility at Level 4 of the Purdue Model; it is a massive electric load at the intersection of global telecommunications, regional power grids, and local water supply systems (UK Parliament, 2025; Chen et al., 2025). Failure to understand these dynamics results in ineffective response and poor coordination between decision-makers (Dudenhoeffer et al., 2006).
The CLAIR Model: Structural Hierarchy and Extended Levels
The CLAIR Model expands the traditional five-level Purdue hierarchy into a ten-level architectural stack. This expansion is designed to capture the "Level -1" dependencies on primary utility infrastructure and the "Level 6" and "Level 7" dependencies on cloud and safety systems (CISA, 2025a; Russo, 2022).
| CLAIR MODEL: 10-Level Architectural Stack | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Level | Layer | Description | Typical assets |
| >7 | High-Trust / Safety Systems | Ultimate integrity & safe-state maintenance | SIS, DNSSEC, Digital root of trust |
| 6 | The Connected World | External cloud & distributed services | AWS/Azure, IIoT platforms,external VPNs |
| 5 | Corporate Enterprise | Business planning & enterprise services | ERP, HR portals, BI/analytics |
| 4 | Business Operations | Resource Management & Workflow Execution | Workflow tools, Data Repositories, Reporting |
| 3.5 | Operational Boundary / Industrial DMZ | IT-OT convergence, traffic filtration, System Integration &Traffic Management | Firewalls, proxies, IPS/IDS, jump hosts, Security Gateways |
| 3 | Site Operations, Local Management | Facility-wide control, monitoring, Real-time System Oversight | Management Servers, Local Configuration Tools, SCADA servers, |
| 2 | Supervisory Control/Direct Control | Local, Immediate System Monitoring & Adjustment | HMI/SCADA clients, User Interfaces, Supervisory Applications |
| 1 | Core Function | Automated regulation & Execution of Primary Tasks | PLCs, RTUs, IEDs, Embedded Logic, Specialized Processors |
| 0 | Environment Interface | Real-time interaction with the physical world | Input/Output Devices, Sensors, Scanners |
| -1 | Primary Infrastructure | External utility generation &distribution | Power grid, Water, Pipelines, Network Backbones, Core Communication |
Level -1: The Primary Infrastructure Foundation
The inclusion of Level -1 acknowledges that the "physics" of Level 0 is entirely dependent on a primary technology layer that exists outside the control of the plant operator (Islam et al., 2023). In the CLAIR Model, Level -1 encompasses the electricity generation and transmission systems, which exhibit complex dynamic behaviors such as low inertia and harmonic distortion when interfacing with data center power electronics (Chen et al., 2025). This layer is the source of cascading failure triggers, where a line fault in the high-voltage grid necessitates immediate load redistribution, often leading to voltage fluctuations that destabilize Level 0 sensors and Level 1 controllers (Islam et al., 2023).
Levels 0-5: What Can Be Controlled
Levels 0–5 are generally within the organization’s direct control because the systems, assets, and processes at these layers are typically owned and/or administered by the business, company, or government entity. However, even within this “control zone,” organizations still inherit external dependencies, especially for software, firmware, and operating systems that rely on vendor-provided patches and updates. If an update is delayed, unavailable, or operationally difficult to deploy, the organization may remain exposed to known vulnerabilities or be forced to rely on temporary mitigations until a corrective patch can be implemented (Souppaya & Scarfone, 2022). As a result, these layers may appear internally controlled while quietly depending on upstream providers and external services that introduce risk across otherwise well-managed environments.
Level 6 and 7: The Distributed Sovereignty
As organizations move toward "Smart Factories" and "Hyperscale Data Centers," the reliance on Level 6 (The Connected World) becomes absolute (CISA, 2025a). This level includes the Cloud-Fog-Edge computing model, where instant processing occurs at the edge but long-term analytics and orchestration reside in the cloud (CISA, 2025a). Level 7 represents the "Safety and High-Trust" layer, which is isolated even from the corporate enterprise to ensure that catastrophic failures at lower levels do not prevent a safe system shutdown (Russo, 2022). Level 7 are systems or items that are critical to restoration of levels 0-6 within the organization. The loss of level 7 is a catastrophic issue.
Integrating Enterprise Architecture: The CLAIR MatrixLinkeIn)
The CLAIR Model maps its ten levels against the six interrogatives of the Zachman Framework to identify dependencies across different dimensions of the infrastructure (The Open Group, n.d.).
- The What (Data and Resource Flow): At the lower levels (-1 to 1), "data" is often a physical resource flow, such as electrons or water pressure (VA DEM, n.d.). At the higher levels (4 to 6), it transitions into digital information payloads (Macaulay, 2025)
- The How (Operational Function): This dimension describes the transformation processes, from ladder logic at Level 1 to machine learning algorithms at Level 6 (CISA, 2025a; Australian Signals Directorate, 2024).
- The Where (Network and Spatial Distribution): This captures geographic interdependencies (Dudenhoeffer et al., 2006). A physical collapse of a pylon destroys both the power source (Level -1) and the communication path (Level 3) sharing that pylon (Islam et al., 2023; VA DEM, n.d.).
- The Who (Stakeholder and Actor Matrix): Maps "managerial independencies" where a Distribution System Operator (DSO) at Level -1 must coordinate with a corporate CIO at Level 5 and a third-party cloud provider at Level 6 (DoD, 2008; Islam et al., 2023).
- The When (Temporal Dynamics): Visualizes the "transient response" during a failure, showing how a grid frequency deviation at Level -1 propagates through the stack faster than a Level 2 supervisory system can respond (Islam et al., 2023; Shuvro et al., 2023).
- The Why (Motivation and Strategy): Identifies where business goals conflict, such as a utility shedding load to save the grid versus a data center's 99.999% availability goal (Mural et al., 2026; The Open Group, n.d.).
Case Study: Power Grid Failures and Data Center Operations
The CLAIR Model demonstrates that power grid failures are not merely physical events; they are systemic crises. Data centers are emerging as prominent large electric loads with demand patterns characterized by high power density (Mural et al., 2026; Chen et al., 2025).
The Mechanism of Cascading Failure
A cascading failure is a sequence where one component malfunction triggers successive failures in a "domino mechanism" (Islam et al., 2023). Within the CLAIR framework:
- The Trigger (Level -1): A disturbance, such as a transmission line failure, occurs in the utility grid (Shuvro et al., 2023).
- Load Redistribution: The grid redistributes flow, but because data centers have massive, steady loads, this can push remaining infrastructure beyond capacity (Mural et al., 2026; Islam et al., 2023).
- Voltage Fluctuations: A sudden fluctuation in Northern Virginia recently triggered the simultaneous disconnection of 60 data centers, creating a 1,500-megawatt (MW) power surplus almost instantly (Mural et al., 2026).
- Information Blindness: As power fails, the cyber network monitoring the grid may also fail. If cloud-based analytics (Level 6) lose connectivity, operators lose visibility, leading to erroneous adjustments and a total blackout (Islam et al., 2023; CISA, 2025a).
Identifying Dependencies: A Typological Deep-Dive
The CLAIR Model categorizes every identified link into a matrix of dependency types. This taxonomy is essential for understanding the nature of the vulnerability.
| Dependency Type | Nature of the Link | Impact Mechanism | Example in CLAIR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical | Material transfer | Functional failure due to lack of inputs | Level -1 power supplying Level 0 servers |
| Cyber | Information transfer | Loss of control or visibility | Level 6 cloud service providing ML insights to Level 1 |
| Geographic | Shared location | Common-cause failure (e.g., flood) | Power and fiber sharing a common utility trench |
| Logical | Policy/Regulation | Change in operational state due to external mandate | Utility load-shedding during a heatwave |
Sankey Flow Maps for Dependency Visualization
To visualize inbound and outbound data dependencies, organizations can use Sankey Flow Maps; flow diagrams that represent transfers or reliance relationships using variable-width links, where wider flows indicate greater magnitude or criticality (Schmidt, 2008). Rather than ranking sensitivities as standalone bars, this method makes dependency direction and coupling immediately visible by placing the system-of-interest at the center and showing weighted flows entering and exiting it.
- Inbound dependencies (inputs to the system): The external data, services, or control-plane functions that the system relies on to operate (e.g., identity assertions, routing/DNS, upstream connectivity, threat intelligence feeds).
- Outbound dependencies (outputs from the system): The downstream systems, users, or business processes that rely on the system’s outputs (e.g., hosted applications/APIs, telemetry to security monitoring, billing/FinOps data).
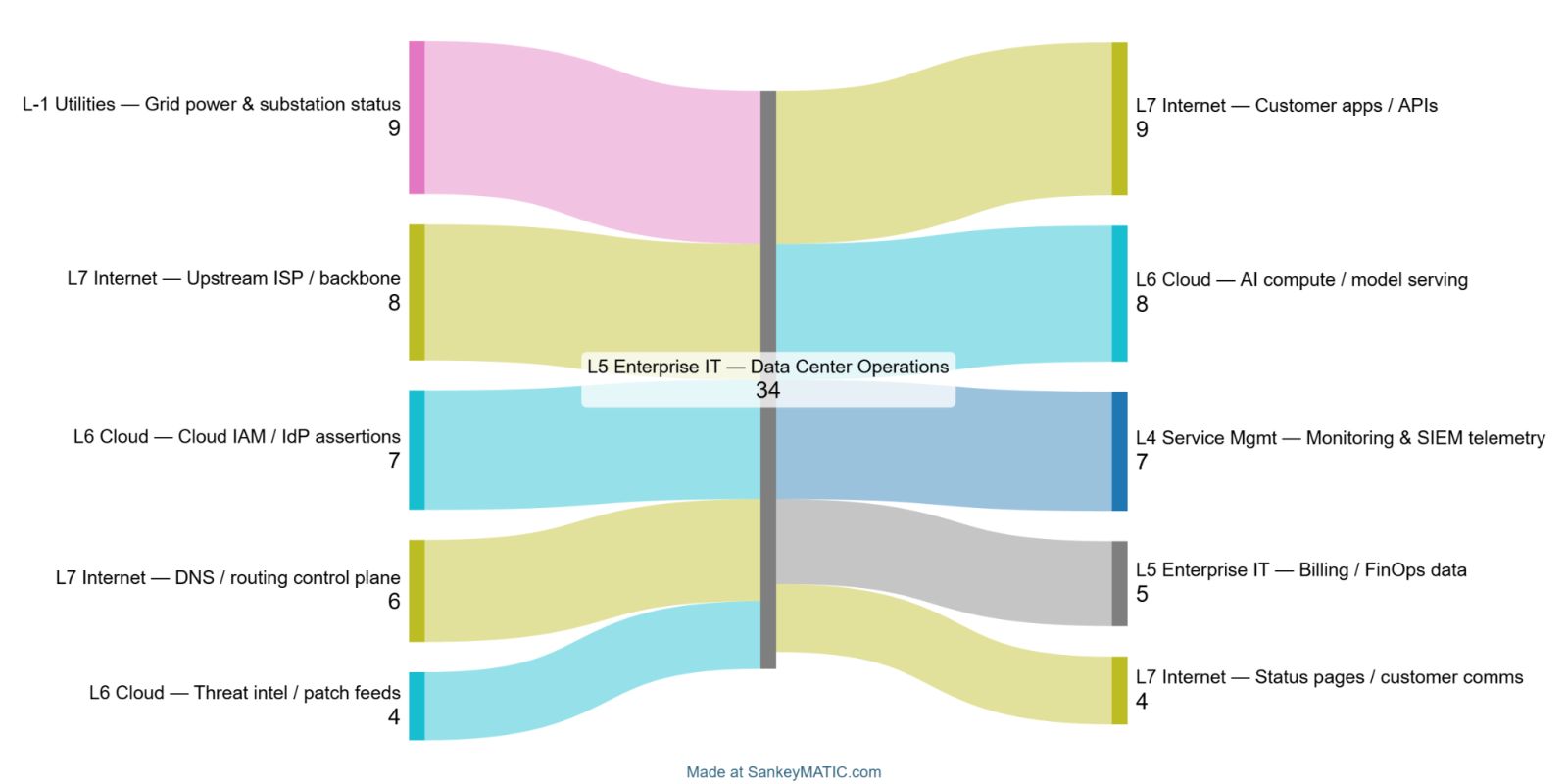 ???????
???????
In practice, each flow can be assigned a dependency “weight” (e.g., criticality, volume, recovery difficulty, or a composite score), enabling teams to quickly identify high-consequence dependencies and prioritize resilience, monitoring, redundancy, and governance controls.
AI as an Interdependency Vector in the CLAIR Model
The integration of AI across levels creates new interdependencies. AI models at the operational layers (0-3) introduce risks such as data quality dependency, model drift, and an explainability gap (ASD, 2024). To maintain resilience, the CLAIR Model incorporates operational constraints like the "80% bandwidth rule," ensuring that data aggregation for AI training does not exceed network capacity to protect critical control signals at Level 1 (ASD, 2024).
AI-OT Convergence Risks
When AI models are deployed at the operational layers (0-3), they introduce failure mechanisms not present in traditional deterministic system:
- Data Quality Dependency: AI models at Level 1 depend on the normalization and quality of sensor data from Level 0. If the sensors are compromised (even at the physics level), the AI will make decisions based on untrusted data.
- Model Drift Dependency: Over time, alterations to production processes can cause an AI model to drift from its initial training. This creates a temporal dependency where the model must be periodically updated from Level 6, creating a cyber-linkage that bypasses the DMZ.
- Explainability Gap: In a crisis, if an AI-driven controller at Level 1 fails or takes an unexpected action, the "Lack of Explainability" increases the operator's recovery time, potentially allowing a local failure to cascade into a regional one.
National Security and Policy Frameworks: The Institutional Why
The "Why" of the CLAIR Model is increasingly driven by policy, such as the National Security Memorandum on Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience (NSM-22) (Congressional Research Service, 2024). This framework groups infrastructure functions into four areas: connect, distribute, manage, and supply, which the CLAIR Model maps to specific assets and their dependencies across the stack (CRS, 2024; CISA, 2025b).Maturity and Assessment in the CLAIR Framework
To evaluate the strength of identified dependencies, the CLAIR Model adopts maturity indicator levels (International Atomic Energy Agency [IAEA], 2021).
Impact on Dependency Risk Real-time visualization across the entire stack
| Maturity Level | Characteristic in CLAIR | |
|---|---|---|
| MIL 0 | No implementation | Opaque dependencies; unpredictable failure |
| MIL 1 | Ad hoc / Informal | Some visibility; no standardized monitoring |
| MIL 2 | Consistent / Monitored | Mapped dependencies; defined failure thresholds |
| MIL 3 | Fully Integrated | |
A key insight is that resilience is only as strong as its weakest link. If a data center has MIL 3 resilience at Level 5 but relies on a Level -1 power source with MIL 0 monitoring, the overall system resilience is effectively MIL 0 (IAEA, 2021).
Conclusion: Visualizing the Interconnected World
The CLAIR Model synthesis of the Purdue Model and Enterprise Architecture moves beyond a narrow view of internal security toward a holistic understanding of infrastructure interdependencies (CISA, 2025a). It demonstrates that the impact of a power grid failure on data centers is multi-dimensional, involving transients at Level -1, sensor failure at Level 0, and business discontinuity at Level 4 (Mural et al., 2026; Islam et al., 2023). By focusing on these linkages, from the physics of the grid to the logic of the cloud, architects can finally visualize the "walking failures" that define our interconnected world (Islam et al., 2023; CISA, 2025b).
References
Australian Signals Directorate. (2024). Principles for the secure integration of artificial intelligence in operational technology. Cyber.gov.au. Accessed January 26, 2026.
Chen, X., Wang, X., Colacelli, A., Lee, M., & Xie, L. (2025). Electricity demand and grid impacts of AI data centers: Challenges and prospects. Accessed January 22, 2026.
Congressional Research Service. (2024). National security memorandum on critical infrastructure security and resilience (NSM-22). Accessed January 28, 2026.
Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency. (2025a). Infrastructure resilience planning framework (IRPF) primer. Accessed January 18, 2026.
Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency. (2025b). Infrastructure resilience planning framework (IRPF) v3.17.2025. Accessed January 30, 2026.
Department of Defense. (2008). Systems engineering guide for systems of systems (Version 1.0). Accessed January 20, 2026. Dudenhoeffer, D. D., Permann, M. R., & Manic, M. (2006).
CIMS: A framework for infrastructure interdependency modeling and analysis. Winter Simulation Conference. Accessed January 23, 2026. Fortinet. (n.d.).
What is the Purdue model for ICS security?. Fortinet.com. Accessed January 13, 2026. International Atomic Energy Agency [IAEA]. (2021).
Maturity-model-paper-ICONS. Accessed January 30, 2026. Islam, M. Z., Lin, Y., Vokkarane, V. M., & Venkataramanan, V. (2023).
Cyber-physical cascading failure and resilience of power grid: A comprehensive review. Frontiers in Energy Research. Accessed January 16, 2026. Macaulay, T. (2025).
The danger of critical infrastructure interdependency. CIGI Online. Accessed January 25, 2026.
Mural, R., Pherwani, D., Gupta, C., Yu, Y., Takahashi, A., Kim, D., Majumder, S., Lee, H., Yu, M., & Xie, L. (2026).
AI, data centers, and the U.S. electric grid: A watershed moment. Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs. Accessed January 15, 2026.
Natural Hazards Review. (2021). Overview of interdependency models of critical infrastructure for resilience assessment (Vol. 23, No. 1). Accessed January 29, 2026.
Russo, S. (2022). Industrial DMZ and zero trust models for ICS. AMS Laurea. Accessed 10 January 24, 2026.
Shuvro, R. A., Das, P., Jyoti, J. S., Abreu, J. M., & Hayat, M. M. (2023). Data-integrity aware stochastic model for cascading failures in power grids. Marquette University. Accessed January 27, 2026.
The Open Group. (n.d.). Mapping the TOGAF ADM to the Zachman framework. Opengroup.org. Accessed January 14, 2026. UK Parliament. (2025).
Data centres: Planning policy, sustainability, and resilience. Accessed January 21, 2026.
Virginia Department of Emergency Management. (n.d.). Understanding critical infrastructure dependencies and interdependencies. Accessed January 17, 2026. Williams, T. J. (1994).
The Purdue enterprise reference architecture (PERA). Industry-Purdue University Consortium. Accessed January 19, 2026. Schmidt, M. (2008).
The Sankey diagram in energy and material flow management, Part I: History. Journal of Industrial Ecology, 12(1), 82–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-9290.2008.00004.x Accessed: February 11, 2026
Souppaya, M., & Scarfone, K. (2022). Guide to enterprise patch management planning: Preventive maintenance for technology (NIST Special Publication 800-40 Rev. 4). National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved January 24, 2026, from https://doi.org/10.6028/NIST.SP.800-40r4


Comments